根据上一篇的介绍,我们已经知道1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10thermoType
{
type heRhoThermo;
mixture pureMixture;
transport const;
thermo hConst;
equationOfState perfectGas;
specie specie;
energy sensibleInternalEnergy;
}
这个设置对应的是下述类:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8heRhoThermo
<
rhoThermo,
pureMixture
<
constTransport<species::thermo<hConstThermo<perfectGas<specie>>,sensibleInternalEnergy>>
>
>
接下来就能来看看具体的类的继承派生关系了。
经过前面的分析,最终指针 thermo_ 指向的是 heRhoThermo 类的对象,所以先来看一下 heRhoThermo 类。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12template<class BasicPsiThermo, class MixtureType>
class heRhoThermo
:
public heThermo<BasicPsiThermo, MixtureType>
{
// Private Member Functions
//- Calculate the thermo variables
void calculate();
//- Construct as copy (not implemented)
heRhoThermo(const heRhoThermo<BasicPsiThermo, MixtureType>&);
heRhoThermo 类很简单,它继承自 heThermo 类,并且和 heThermo 类用同样的模板参数。
接下来看看 heThermo 类:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12template<class BasicThermo, class MixtureType>
class heThermo
:
public BasicThermo,
public MixtureType
{
protected:
// Protected data
//- Energy field
volScalarField he_;
这里,前面多次提到的“继承其模板参数代表的类”这种模式又出现了。有了前两篇分析的基础,我们已经知晓了 thermophysicalProperties 文件里的设置将对应着怎么的一个具体的模型,所有的模板参数都一目了然。知道了模板参数,就能将模板类实例化,再分析其继承派生关系就不是问题了。探索的中间过程这里不详述了,只列出文章开头的那个实例对应的继承派生关系:
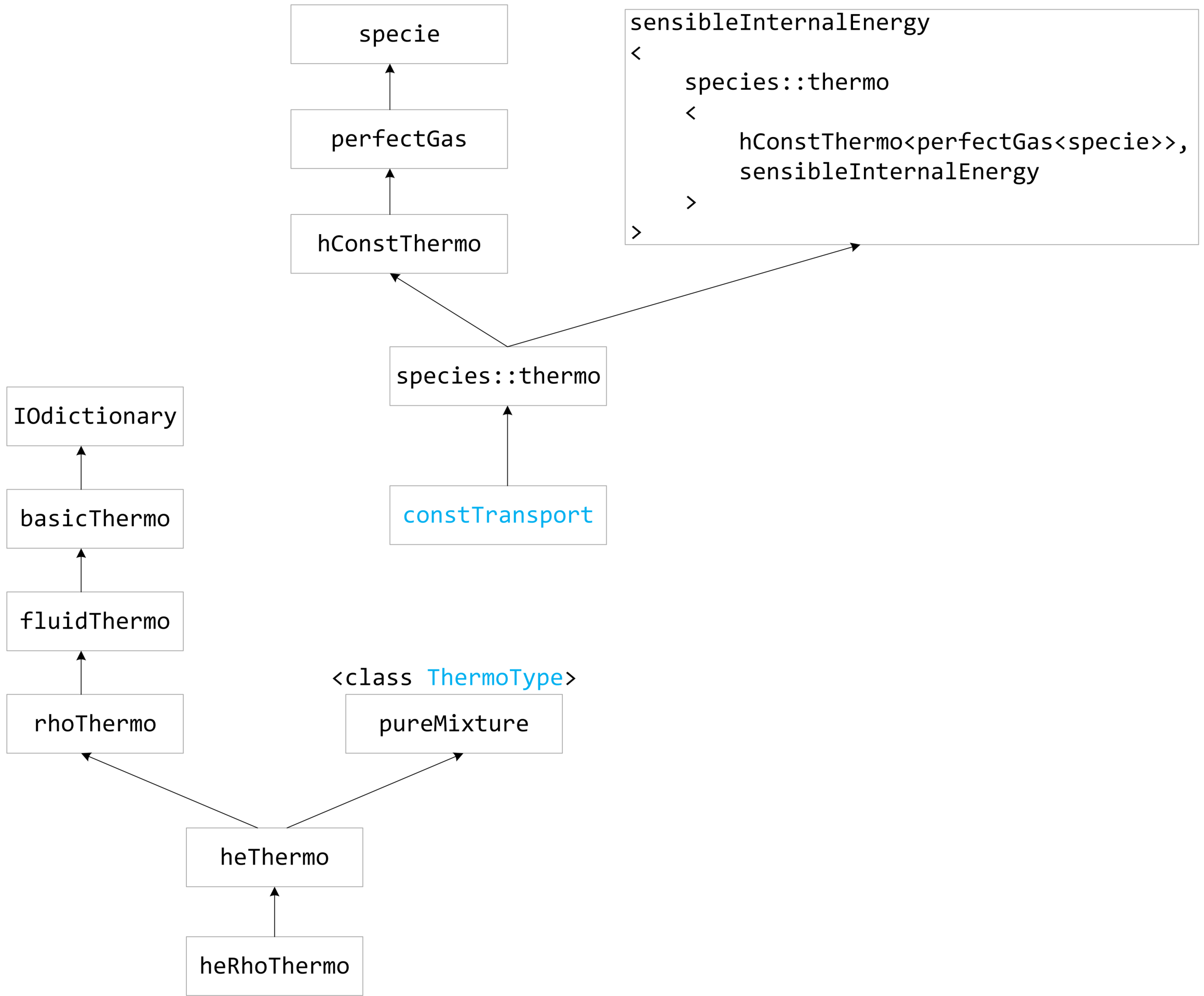
注意几点:
- 上图中有两个继承派生关系,其中
constTransport这个类是作为pureMixture类的模板参数的,从而将这两个部分联系起来。 species::thermo中,species是命名空间,thermo是类名,具体定义在src/thermophysicalModels/specie/thermo/thermo/thermo.H。sensibleInternalEnergy类的模板参数中,某种程度上讲,包含了它自己!- mixture,transport,thermo,equationOfstate,specie,energy 这 6 个子模型有哪些可选的,这一点在 UserGuide 的第 7 章已经介绍得很清楚了,这里就不再重复了。
了解了这些,就能理解热物理类的框架了。下一部分将针对 twoPhaseEulerFoam 的热物理相关的模块,来梳理一下热物理模型的流程,主要是,能量方程的构建,如何从能量来得到温度,其他依赖于温度的量包括粘度、密度、压力等又是如何更新的,希望能对传热的模拟有些指导作用,尤其是当出问题的时候,能大概知道可能的原因。