JohnsonJackson 边界条件
本篇来看用于气固两相流模拟的 JohnsonJackson 边界条件。这组边界条件用于设定双流体模型中固相在壁面的速度和颗粒温度。根据 N. Reuge 2008, CES,壁面上的固相速度和颗粒温度可以表示为: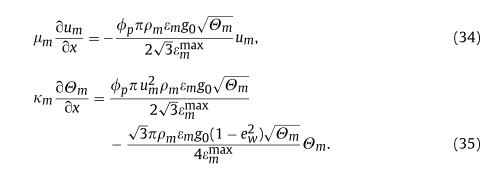
其中,$u_m$ 指的是 m 相在壁面切向上的滑移速度。
下面来看 OpenFOAM 中对这两个边界条件的实现
在看 JohnsonJackson 边界条件之前,先要看一下 partialSlip 边界。
partialSlip
partialSlipFvPatchField 继承自 transformFvPatchField1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11template<class Type>
class partialSlipFvPatchField
:
public transformFvPatchField<Type>
{
// Private data
//- Fraction (0-1) of value used for boundary condition
scalarField valueFraction_;
......
}
其定义了一个标量形式的 valueFraction_ 。
- evaluate 函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21template<class Type>
void Foam::partialSlipFvPatchField<Type>::evaluate
(
const Pstream::commsTypes
)
{
if (!this->updated())
{
this->updateCoeffs();
}
tmp<vectorField> nHat = this->patch().nf();
Field<Type>::operator=
(
(1.0 - valueFraction_)
*transform(I - sqr(nHat), this->patchInternalField())
);
transformFvPatchField<Type>::evaluate();
}
与 basicSymmetry 相比,只是多了一项 1.0 - valueFraction_ 。当 valueFraction_ = 0 时,其与 basicSymmetry 是一样的。
- snGradTransformDiag
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16template<class Type>
Foam::tmp<Foam::Field<Type> >
Foam::partialSlipFvPatchField<Type>::snGradTransformDiag() const
{
const vectorField nHat(this->patch().nf());
vectorField diag(nHat.size());
diag.replace(vector::X, mag(nHat.component(vector::X)));
diag.replace(vector::Y, mag(nHat.component(vector::Y)));
diag.replace(vector::Z, mag(nHat.component(vector::Z)));
return
valueFraction_*pTraits<Type>::one
+ (1.0 - valueFraction_)
*transformFieldMask<Type>(pow<vector, pTraits<Type>::rank>(diag));
}
当 valueFraction_ = 0 时,这里的返回值与 basicSymmetry 也是一样的。
- snGrad
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12template<class Type>
Foam::tmp<Foam::Field<Type> >
Foam::partialSlipFvPatchField<Type>::snGrad() const
{
tmp<vectorField> nHat = this->patch().nf();
const Field<Type> pif(this->patchInternalField());
return
(
(1.0 - valueFraction_)*transform(I - sqr(nHat), pif) - pif
)*this->patch().deltaCoeffs();
}
User guide 里说这个边界是 slip 和 zeroGradient 的混合。 valueFraction_ = 0 时, partialSlip 与 slip 等价,这一点上面说明了。不过, 另一个极端,valueFraction_ = 1 时,却似乎不是跟 zeroGradient 等价。至少, evaluate 函数在valueFraction_ = 1 时与 zeroGradient 中的是不一样的。
这里提到了 slip 这个边界,顺便再说一下, slip 边界继承自 basicSymmetry ,而且没有增加任何新的定义,所以, slip 与 basicSymmetry 的效果是等价的。对于标量, slip 与 zeroGradient 一样;对于矢量,以速度为例, slip 定义的边界上的速度值等于边界所属网格的速度的平行边界的分量,即
$$
u_p = u_C - (\overrightarrow{n} \otimes \overrightarrow{n})\cdot u_C
$$
JohnsonJacksonParticleSlip
这个边界条件继承自 partialSlip,在此基础上额外定义了镜面反弹系数 specularityCoefficient_ 。代码的核心在 updateCoeffs 函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84void Foam::JohnsonJacksonParticleSlipFvPatchVectorField::updateCoeffs()
{
if (updated())
{
return;
}
// lookup the fluid model and the phase
const twoPhaseSystem& fluid = db().lookupObject<twoPhaseSystem>
(
"phaseProperties"
);
const phaseModel& phased
(
fluid.phase1().name() == dimensionedInternalField().group()
? fluid.phase1()
: fluid.phase2()
);
// lookup all the fields on this patch
const fvPatchScalarField& alpha
(
patch().lookupPatchField<volScalarField, scalar>
(
phased.volScalarField::name()
)
);
const fvPatchScalarField& gs0
(
patch().lookupPatchField<volScalarField, scalar>
(
IOobject::groupName("gs0", phased.name())
)
);
const scalarField nu
(
patch().lookupPatchField<volScalarField, scalar>
(
IOobject::groupName("nut", phased.name())
)
);
word ThetaName(IOobject::groupName("Theta", phased.name()));
const fvPatchScalarField& Theta
(
db().foundObject<volScalarField>(ThetaName)
? patch().lookupPatchField<volScalarField, scalar>(ThetaName)
: alpha
);
// lookup the packed volume fraction
dimensionedScalar alphaMax
(
"alphaMax",
dimless,
db()
.lookupObject<IOdictionary>
(
IOobject::groupName("turbulenceProperties", phased.name())
)
.subDict("RAS")
.subDict("kineticTheoryCoeffs")
.lookup("alphaMax")
);
// calculate the slip value fraction
scalarField c
(
constant::mathematical::pi
*alpha
*gs0
*specularityCoefficient_.value()
*sqrt(3.0*Theta)
/max(6.0*nu*alphaMax.value(), SMALL)
);
this->valueFraction() = c/(c + patch().deltaCoeffs());
partialSlipFvPatchVectorField::updateCoeffs();
}
这个函数主要的功能是重定义了继承自 partialSlip 中的 valueFraction_。结合 partialSlip 中的定义,可以知道最终 JohnsonJacksonParticleSlip 定义的边界速度的值为
$$
u_m=(1-\frac{c}{c+\Delta}) \cdot (\mathbf{I}-\overrightarrow{n}\otimes\overrightarrow{n})\cdot u_c
$$
其中 $u_c$ 为邻近壁面网格的 m 相的速度。c 的定义为:
$$
c=\frac{\pi \varepsilon_m g_0 \phi\sqrt{3\Theta}}{6.0\nu_m\varepsilon_m^{max}}
$$
对照上述公式(34),根据 $c$ 的定义,这里可以把公式(34)简写为
$$
\frac{\partial u_m}{\partial x}=-cu_m
$$
写成差分形式,即
$$
(u_m-u_{ct})\cdot \Delta=-cu_m
$$
于是得到
$$
u_m = \frac{\Delta}{c+\Delta}u_{ct}
$$
若 $u_{ct}$ 定义为邻近壁面网格的速度壁面切向分量,则公式(34)与代码是一致的。
JohnsonJacksonParticleTheta
这个边界条件继承自 mixed ,此外新增了两个数据成员: specularityCoefficient_ 和 restitutionCoefficient_ 。核心的函数也是 updateCoeffs 。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114void Foam::JohnsonJacksonParticleThetaFvPatchScalarField::updateCoeffs()
{
if (updated())
{
return;
}
// lookup the fluid model and the phase
const twoPhaseSystem& fluid = db().lookupObject<twoPhaseSystem>
(
"phaseProperties"
);
const phaseModel& phased
(
fluid.phase1().name() == dimensionedInternalField().group()
? fluid.phase1()
: fluid.phase2()
);
// lookup all the fields on this patch
const fvPatchScalarField& alpha
(
patch().lookupPatchField<volScalarField, scalar>
(
phased.volScalarField::name()
)
);
const fvPatchVectorField& U
(
patch().lookupPatchField<volVectorField, vector>
(
IOobject::groupName("U", phased.name())
)
);
const fvPatchScalarField& gs0
(
patch().lookupPatchField<volScalarField, scalar>
(
IOobject::groupName("gs0", phased.name())
)
);
const fvPatchScalarField& kappa
(
patch().lookupPatchField<volScalarField, scalar>
(
IOobject::groupName("kappa", phased.name())
)
);
const scalarField Theta(patchInternalField());
// lookup the packed volume fraction
dimensionedScalar alphaMax
(
"alphaMax",
dimless,
db()
.lookupObject<IOdictionary>
(
IOobject::groupName("turbulenceProperties", phased.name())
)
.subDict("RAS")
.subDict("kineticTheoryCoeffs")
.lookup("alphaMax")
);
// calculate the reference value and the value fraction
if (restitutionCoefficient_.value() != 1.0)
{
this->refValue() =
(2.0/3.0)
*specularityCoefficient_.value()
*magSqr(U)
/(scalar(1) - sqr(restitutionCoefficient_.value()));
this->refGrad() = 0.0;
scalarField c
(
constant::mathematical::pi
*alpha
*gs0
*(scalar(1) - sqr(restitutionCoefficient_.value()))
*sqrt(3.0*Theta)
/max(4.0*kappa*alphaMax.value(), SMALL)
);
this->valueFraction() = c/(c + patch().deltaCoeffs());
}
// for a restitution coefficient of 1, the boundary degenerates to a fixed
// gradient condition
else
{
this->refValue() = 0.0;
this->refGrad() =
pos(alpha - SMALL)
*constant::mathematical::pi
*specularityCoefficient_.value()
*alpha
*gs0
*sqrt(3.0*Theta)
*magSqr(U)
/max(6.0*kappa*alphaMax.value(), SMALL);
this->valueFraction() = 0.0;
}
mixedFvPatchScalarField::updateCoeffs();
}
这里分两种情况,即 restitutionCoefficient_ 是否等于1。其实从公式(35)也能看出来,$e_w=1$ 与 $e_w \neq 1$ 是不一样的。
$e_w\neq 1$
这时,重定义了refValue和valueFraction。利用辅助变量 $c$ 的定义,可以将公式(35)简化如下:
$$
\frac{\partial \Theta_m}{\partial x}=c \cdot refValue - c \cdot \Theta_m
$$
写成差分形式
$$
(\Theta_m-\Theta_c) \cdot \Delta = c\cdot refValue - c \cdot \Theta_m
$$
得
$$
\Theta_m=\frac{c}{c+\Delta}\cdot refValue + \frac{\Delta}{c+\Delta} \cdot \Theta_c
$$
其中 $\Theta_c$ 为邻近壁面网格的颗粒温度。
根据mixed的定义,壁面的值应当是valureFraction * refValue + (1-valueFraction)*(patchInternalField() + refGrad/delta)。 这里将refGrad赋值为0,就与公式一致了。$e_w = 1$
这种情况下,JohnsonJacksonParticleTheta就退化为简单的fixedGradient了。若 $ \varepsilon_m $ 特别小,则为零梯度,否则,固定梯度,梯度值等于公式(35)的右边第一项。