在 kineticTheoryModel 类的解读时前面提到过, kineticTheoryModel 使用了跟湍流模型一样的接口。这一篇,就来看一下 twoPhaseEulerFoam 中的湍流模型。
OpenFOAM-2.3.x 中的twoPhaseEulerFoam 流体相可以调用 RAS 和 LES 湍流模型,固相可以使用两种计算固相应力的“湍流模型”。
湍流模型的调用是通过 phaseModel 来进行的,具体的过程放到最后来讲,这里先说一下最重要的 divDevRhoReff 函数的形式,主要有三种类型:用于固相的 phasePressure 和 kineticTheoryModel 以及用于流体相的 RAS 模型或 LES 模型,以 kEpsilon 模型为例。此外,在”pEqn.H”里,还需要用到 pPrime() 函数,这个函数主要是在处理颗粒相的压力时有意义,所以,在 phasePressure 和 kineticTheoryModel 两个模型中,这个函数也需要关注一下。
1 phasePressure
很显然,这个是用于固相的,只考虑所谓固相压力,所以理论上, divDevRhoReff函数应该是对固相动量方程没有贡献的,实际上也正是如此,其定义如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15Foam::tmp<Foam::fvVectorMatrix>
Foam::RASModels::phasePressureModel::divDevRhoReff
(
volVectorField& U
) const
{
return tmp<fvVectorMatrix>
(
new fvVectorMatrix
(
U,
this->rho_.dimensions()*dimensionSet(0, 4, -2, 0, 0)
)
);
}
经测验,这一项对 fvVectorMatrix 的贡献是零。
1 | Foam::tmp<Foam::volScalarField> |
phasePressure 模型计算的“固相压力”为
$$
pPrime = g0\cdot \mathrm{min}(e^{preAlphaExp\cdot (\varepsilon_s - \varepsilon_{s,max})},expMax)
$$
注意这里的$g0$ 与 radialModel 中的$g_0$ 不是一个概念!
2 kineticTheory
KTGF 模型, 代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74 Foam::tmp<Foam::fvVectorMatrix>
Foam::RASModels::kineticTheoryModel::divDevRhoReff
(
volVectorField& U
) const
{
return
(
- fvm::laplacian(this->rho_*this->nut_, U)
- fvc::div
(
(this->rho_*this->nut_)*dev2(T(fvc::grad(U)))
+ ((this->rho_*lambda_)*fvc::div(this->phi_))
*dimensioned<symmTensor>("I", dimless, symmTensor::I)
)
);
}
Foam::tmp<Foam::volScalarField>
Foam::RASModels::kineticTheoryModel::pPrime() const
{
// Local references
const volScalarField& alpha = this->alpha_;
const volScalarField& rho = phase_.rho();
return
(
Theta_
*granularPressureModel_->granularPressureCoeffPrime
(
alpha,
radialModel_->g0(alpha, alphaMinFriction_, alphaMax_),
radialModel_->g0prime(alpha, alphaMinFriction_, alphaMax_),
rho,
e_
)
+ frictionalStressModel_->frictionalPressurePrime
(
alpha,
alphaMinFriction_,
alphaMax_
)
);
}
Foam::tmp<Foam::surfaceScalarField>
Foam::RASModels::kineticTheoryModel::pPrimef() const
{
// Local references
const volScalarField& alpha = this->alpha_;
const volScalarField& rho = phase_.rho();
return fvc::interpolate
(
Theta_
*granularPressureModel_->granularPressureCoeffPrime
(
alpha,
radialModel_->g0(alpha, alphaMinFriction_, alphaMax_),
radialModel_->g0prime(alpha, alphaMinFriction_, alphaMax_),
rho,
e_
)
+ frictionalStressModel_->frictionalPressurePrime
(
alpha,
alphaMinFriction_,
alphaMax_
)
);
}
这一部分详细的公式已在 kineticTheoryModel 解读部分分析了,不再赘述。
3 kEpsilon (OpenFOAM-2.3.x/src/TurbulenceModels/turbulenceModels/RAS/kEpsilon)
这个代表的是RAS湍流模型。(其实还有 LES 模型,只是 RAS 与 LES 的 divDevRhoReff函数形式应该是一样的),函数所在代码路径为:OpenFOAM-2.3.x/src/TurbulenceModels/turbulenceModels/eddyViscosity/eddyViscosity.C
1 | template<class BasicTurbulenceModel> |
kEpsilon 类中没有重新定义 pPrime() 函数,而是直接继承 PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel 类中的定义,返回零,这里就不列出代码了。
湍流模型的调用
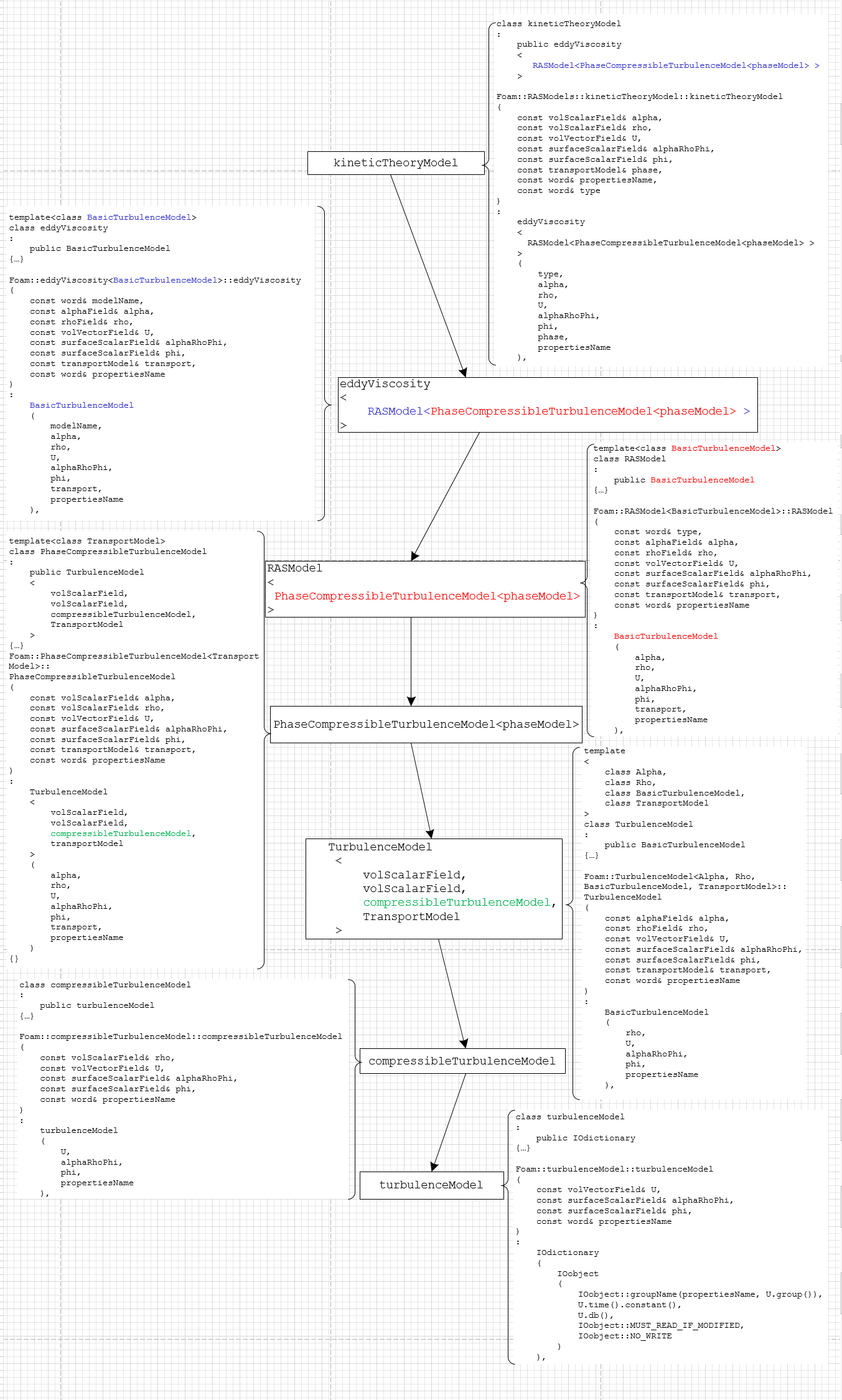
湍流模型的调用过程,值得看一下,重点是看一下湍流模型类的继承派生关系,以 kineticTheoryModel 为例。kineticTheoryModel 类的声明和构造函数部分如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34class kineticTheoryModel
:
public eddyViscosity
<
RASModel<PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel<phaseModel> >
>
{
......
}
Foam::RASModels::kineticTheoryModel::kineticTheoryModel
(
const volScalarField& alpha,
const volScalarField& rho,
const volVectorField& U,
const surfaceScalarField& alphaRhoPhi,
const surfaceScalarField& phi,
const transportModel& phase,
const word& propertiesName,
const word& type
)
:
eddyViscosity<RASModel<PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel<phaseModel> > >
(
type,
alpha,
rho,
U,
alphaRhoPhi,
phi,
phase,
propertiesName
),
......
可见, kineticTheoryModel 类继承自 eddyViscosity 类,并且用 RASModel<PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel<phaseModel> > 来实例化eddyViscosity 类中的模板参数。
再来看eddyViscosity 类:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52template<class BasicTurbulenceModel>
class eddyViscosity
:
public BasicTurbulenceModel
{
protected:
// Protected data
// Fields
volScalarField nut_;
// Protected Member Functions
virtual void correctNut() = 0;
template<class BasicTurbulenceModel>
Foam::eddyViscosity<BasicTurbulenceModel>::eddyViscosity
(
const word& modelName,
const alphaField& alpha,
const rhoField& rho,
const volVectorField& U,
const surfaceScalarField& alphaRhoPhi,
const surfaceScalarField& phi,
const transportModel& transport,
const word& propertiesName
)
:
BasicTurbulenceModel
(
modelName,
alpha,
rho,
U,
alphaRhoPhi,
phi,
transport,
propertiesName
),
nut_
(
IOobject
(
IOobject::groupName("nut", U.group()),
this->runTime_.timeName(),
this->mesh_,
IOobject::MUST_READ,
IOobject::AUTO_WRITE
),
this->mesh_
)
{}
注意,这里有意思的来了, eddyViscosity 类继承自其模板参数代表的类,具体继承自哪个类,要等模板实例化了才知道。这种用法我还是头一次接触。根据上面 kineticTheoryModel 类的构造函数,可知 eddyViscosity 类在当前分析的情况下,将继承自 RASModel<PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel<phaseModel> > 。
继续看 RASModel 类的定义:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101template<class BasicTurbulenceModel>
class RASModel
:
public BasicTurbulenceModel
{
protected:
// Protected data
//- RAS coefficients dictionary
dictionary RASDict_;
//- Turbulence on/off flag
Switch turbulence_;
//- Flag to print the model coeffs at run-time
Switch printCoeffs_;
//- Model coefficients dictionary
dictionary coeffDict_;
//- Lower limit of k
dimensionedScalar kMin_;
//- Lower limit of epsilon
dimensionedScalar epsilonMin_;
//- Lower limit for omega
dimensionedScalar omegaMin_;
......
};
// constructor
template<class BasicTurbulenceModel>
Foam::RASModel<BasicTurbulenceModel>::RASModel
(
const word& type,
const alphaField& alpha,
const rhoField& rho,
const volVectorField& U,
const surfaceScalarField& alphaRhoPhi,
const surfaceScalarField& phi,
const transportModel& transport,
const word& propertiesName
)
:
BasicTurbulenceModel
(
alpha,
rho,
U,
alphaRhoPhi,
phi,
transport,
propertiesName
),
RASDict_(this->subOrEmptyDict("RAS")),
turbulence_(RASDict_.lookup("turbulence")),
printCoeffs_(RASDict_.lookupOrDefault<Switch>("printCoeffs", false)),
coeffDict_(RASDict_.subOrEmptyDict(type + "Coeffs")),
kMin_
(
dimensioned<scalar>::lookupOrAddToDict
(
"kMin",
RASDict_,
SMALL,
sqr(dimVelocity)
)
),
epsilonMin_
(
dimensioned<scalar>::lookupOrAddToDict
(
"epsilonMin",
RASDict_,
SMALL,
kMin_.dimensions()/dimTime
)
),
omegaMin_
(
dimensioned<scalar>::lookupOrAddToDict
(
"omegaMin",
RASDict_,
SMALL,
dimless/dimTime
)
)
{
// Force the construction of the mesh deltaCoeffs which may be needed
// for the construction of the derived models and BCs
this->mesh_.deltaCoeffs();
}
RASModel 类也是继承自模板参数代表的类,在这里分析的情况下,模板参数将实例化为 PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel<phaseModel> ,所以, RASModel 类也将继承自 PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel<phaseModel>。
PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel 类定义如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51template<class TransportModel>
class PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel
:
public TurbulenceModel
<
volScalarField,
volScalarField,
compressibleTurbulenceModel,
TransportModel
>
{
public:
typedef volScalarField alphaField;
typedef volScalarField rhoField;
typedef TransportModel transportModel;
......
......
};
template<class TransportModel>
Foam::PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel<TransportModel>::
PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel
(
const volScalarField& alpha,
const volScalarField& rho,
const volVectorField& U,
const surfaceScalarField& alphaRhoPhi,
const surfaceScalarField& phi,
const transportModel& transport,
const word& propertiesName
)
:
TurbulenceModel
<
volScalarField,
volScalarField,
compressibleTurbulenceModel,
transportModel
>
(
alpha,
rho,
U,
alphaRhoPhi,
phi,
transport,
propertiesName
)
{}
可见, PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel 类继承自 TurbulenceModel 类,并且要注意给 TurbulenceModel 的模板代入的实例化参数。
继续深入,来看 TurbulenceModel 的定义,1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59template
<
class Alpha,
class Rho,
class BasicTurbulenceModel,
class TransportModel
>
class TurbulenceModel
:
public BasicTurbulenceModel
{
public:
typedef Alpha alphaField;
typedef Rho rhoField;
typedef TransportModel transportModel;
protected:
// Protected data
const alphaField& alpha_;
const transportModel& transport_;
......
......
};
template
<
class Alpha,
class Rho,
class BasicTurbulenceModel,
class TransportModel
>
Foam::TurbulenceModel<Alpha, Rho, BasicTurbulenceModel, TransportModel>::
TurbulenceModel
(
const alphaField& alpha,
const rhoField& rho,
const volVectorField& U,
const surfaceScalarField& alphaRhoPhi,
const surfaceScalarField& phi,
const transportModel& transport,
const word& propertiesName
)
:
BasicTurbulenceModel
(
rho,
U,
alphaRhoPhi,
phi,
propertiesName
),
alpha_(alpha),
transport_(transport)
{}
TurbulenceModel 继承自模板的第三个参数对应的类,从 PhaseCompressibleTurbulenceModel 的定义可知,这里是 compressibleTurbulenceModel 。此外,还要注意这个类有一个数据成员是 alpha_,在派生类的某些地方会调用这个数据成员。
接着再看, compressibleTurbulenceModel,1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32class compressibleTurbulenceModel
:
public turbulenceModel
{
protected:
// Protected data
const volScalarField& rho_;
......
......
};
Foam::compressibleTurbulenceModel::compressibleTurbulenceModel
(
const volScalarField& rho,
const volVectorField& U,
const surfaceScalarField& alphaRhoPhi,
const surfaceScalarField& phi,
const word& propertiesName
)
:
turbulenceModel
(
U,
alphaRhoPhi,
phi,
propertiesName
),
rho_(rho)
{}
这个类继承自 turbulenceModel ,并且有一个数据成员 rho_ 。
最底层的是 turbulenceModel 类了,其定义如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49class turbulenceModel
:
public IOdictionary
{
protected:
// Protected data
const Time& runTime_;
const fvMesh& mesh_;
const volVectorField& U_;
const surfaceScalarField& alphaRhoPhi_;
const surfaceScalarField& phi_;
//- Near wall distance boundary field
nearWallDist y_;
......
......
};
Foam::turbulenceModel::turbulenceModel
(
const volVectorField& U,
const surfaceScalarField& alphaRhoPhi,
const surfaceScalarField& phi,
const word& propertiesName
)
:
IOdictionary
(
IOobject
(
IOobject::groupName(propertiesName, U.group()),
U.time().constant(),
U.db(),
IOobject::MUST_READ_IF_MODIFIED,
IOobject::NO_WRITE
)
),
runTime_(U.time()),
mesh_(U.mesh()),
U_(U),
alphaRhoPhi_(alphaRhoPhi),
phi_(phi),
y_(mesh_)
{}
这个类里定义了数据成员 U_,在 kineticTheoryModel 类中用到了。
总结一下,湍流模型的继承派生关系如下图(看大图请右键点击图片,选“在新标签页中打开”):
像上面这种“类继承其模板参数所代表的类”的用法,在 OpenFOAM 中使用很普遍,最近在看的 thermodynamics 相关的代码里也大量使用了这种模式。不知道这是不是一种 C++ 的 design pattern?这方面我的理解还很浅显。